A detailed guide
Hybrid cloud architecture
Dialpad's AI-powered communications platform is built on a unique dual cloud architecture that's designed to give you excellent call quality around the world. Book a product tour to get a walkthrough of how to keep data secure while allowing employees to work from anywhere with cloud communications.

In today’s age of digital transformation, the cloud reigns supreme.
Cloud migration allows businesses of all shapes and sizes to access enterprise-grade technology, applications, and features. Cloud computing, including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS) solutions, offers countless benefits for modern organizations, including increased flexibility, cost savings, improved operational efficiency, and so on.
When it comes to cloud infrastructure, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. If you’re considering switching to the cloud, you’ll need a good understanding of the different types of cloud architecture.
One type of cloud infrastructure popular among modern businesses due to its security and flexibility is the hybrid cloud.
In this guide, we’ll break down what hybrid cloud architecture is, and when it might be the right choice for an organization.
The 3 main types of cloud
Public cloud
The public cloud is a cloud computing model in which cloud resources, including servers and storage, are owned and managed by third-party public cloud providers and delivered via the internet.
Public cloud infrastructure can be accessed by any user who passes the appropriate authentication checks.
This is the most popular type of cloud computing service. Public cloud services are usually offered as software as a service (SaaS), or platform as a service (PaaS) managed services. Examples of public cloud providers include Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services (AWS).
So, what are some defining characteristics of public cloud services? Well, there are a few.
Flexibility and scalability to meet your business needs
Maintenance is taken care of by the service provider
Low costs, since there’s no need to purchase hardware or software
You pay for the services you use (typically free or subscription-based pricing tier)
Private cloud
The private cloud refers to a cloud computing environment where cloud computing resources can only be accessed or used by a single organization or business. So core employees can use servers and storage, but anyone outside of the organization can’t.
Private clouds can be located in your organization’s on-premises data center or hosted in an off-premises environment by a third-party vendor. However, in a private cloud, services and infrastructure are delivered on a secure private network, and cloud computing resources are dedicated solely to your business.
For this reason, private clouds are used by organizations that store hyper-sensitive data, such as financial institutions, government agencies, and healthcare providers.
Here are some hallmarks of private clouds:
The ability to optimize control over the business environment and cloud resources
Maximum visibility into the overall cloud infrastructure
Customizability to meet unique business needs
Increased security, since access is heavily restricted
Servers are located in-house or hosted by third-party service providers
An example
Let’s say you want to host a new website. You go shopping around for a low cost service and find a website hosting company that offers a “dedicated” website for $5.99 a month. Great price, right? It’s so inexpensive because you are sharing a “server” with a lot of other customers—your processor, RAM, and hard drive space are shared with that hosting company’s other customers. This is public cloud.
Now, your business and website is growing and growing and getting more complex with lots of clicky buttons and fancy stuff. It’s time to step up your cloud orchestration and get a dedicated server to handle this: or, private cloud. You could create a server in your data center or headquarters, but let’s say this same hosting company offers you a dedicated server package and you move some of the “fancy clicky buttons” to it. Now, you’re on a private cloud, since the computer, RAM, hard drive, and processor are dedicated only to your company.
Once you connect the “fancy clicky button” processes from the private cloud server to the website on the public cloud, you’ve entered the “hybrid cloud” universe.
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud environment is an IT infrastructure that combines the best of both worlds by blending public and private clouds. This allows data and apps to move between both cloud environments so that some functions take place in the private cloud and others in the public cloud. You can choose which option is best suited to each application and can shift workloads between the two as required.
Hybrid cloud solutions are popular with businesses that need to meet regulatory data requirements by storing sensitive data in the private cloud—while benefiting from the public cloud’s flexibility and scalability.
👉 Dialpad tip:
Let’s take this website hosting story a bit further. Now you have a hybrid cloud setup (with a dedicated server), but you want to add in 12 million-billion documents that your customers can download. Using the hosting company’s storage would be astronomical in price (a bazillion dollars). So you decide to use your data center servers as the place where they are stored. You set up a secure and dedicated connection from your data center to the public cloud servers so the files can be accessed. People out in the world can’t directly grab them, but your web server can. Now, you’ve connected the private cloud server with the public cloud web server and your data center servers… And truly extended the reach of public and private cloud offerings.
What is hybrid cloud architecture?
The term hybrid cloud architecture describes the combined use of private and public clouds, as well as on-premises computing. Hybrid cloud architecture should connect multiple computers, be scalable, and allow workloads and cloud resources to be moved from one cloud environment to the other seamlessly.
Private, public, and hybrid clouds all share the same basic cloud infrastructure, which includes:
Connection: Cloud environments link multiple computers and devices through the use of a local area network (LAN), wide area network (WAN), virtual private network (VPN), or Application Programming Interface (API).
Infrastructure: All the hardware components of traditional data centers, including servers, storage, and networking gear (such as routers and switches).
Middleware: Software components like databases and business communications apps that enable communication between networked computers, apps, and software.
Data management tools: These tools allow businesses and service providers to monitor the cloud environment’s performance and storage capacity so IT teams can track usage, ensure disaster recovery, and deploy apps from a centralized console.
Automation: Software that facilitates the delivery of IT services through automation to ease workloads, reduce costs, streamline operations, and scale cloud resources.
Another cloud computing model to be aware of is multi-cloud architecture. Multi-cloud architecture uses multiple public cloud services to improve flexibility by allowing businesses to deploy cloud services that meet their business requirements. This also reduces the reliance on single cloud vendors for increased cost savings.
And there are different types of hybrid cloud models too, including:
Tiered hybrid: This allows you to deploy existing applications in the public cloud but keep your computing in your private cloud
Edge hybrid: Edge computing fits in across hybrid and multi-cloud architecture and involves running servers nearer to where data is created. This requires each device on a LAN network to play a part in processing information. This is often referred to as a CDN: Content Delivery Network. There are lots of providers who offer CDN services for almost anything you can think of—Google GCP, Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, etc...
Cloud bursting: This enables you to keep applications in the private cloud while also enabling you to move applications to the public cloud when you experience a surge in demand
What is Dialpad? Public, private, or hybrid?
Dialpad is a cloud-hosted platform and uses private cloud architecture. Everything is built on the Google Cloud Platform, which provides unmatched security and reliability and allows us to scale and modify your Dialpad instance depending on traffic size, so we can grow with you while preventing overprovisioning of services.
Our strategically placed global data centers help us deliver all your business media needs including voice, video, and messaging, with high-definition audio quality, high availability, and low latency no matter where in the world you’re calling from.
We call this “dual-cloud architecture” and it’s one of the things that make Dialpad unique. We use private cloud services from GCP that can scale and grow and flex with demand, and our dedicated data centers for the best quality voice and video:
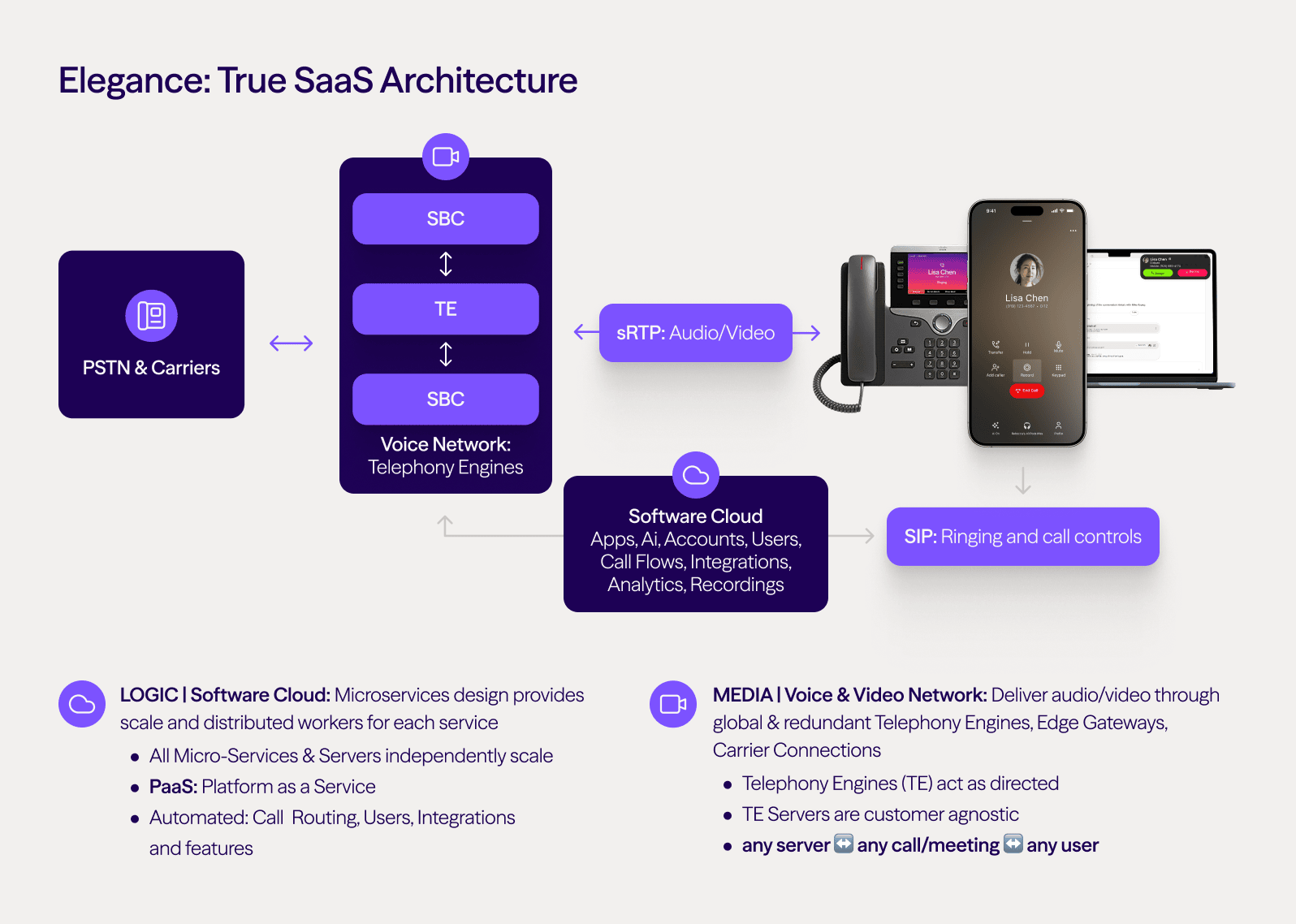
No matter where your team is working from or which device or operating system they’re using, you’ll get a secure and scalable business communications platform that includes virtual phone system features, video conferencing, and contact center functionality to help you connect and collaborate more productively.
🧠 What's keeping CIOs up at night?
We interviewed 12 CIOs across a range of industries like healthcare, law, and higher ed. Get the playbook to learn about their approaches to data security, hybrid work, and more!
The benefits of hybrid cloud architecture
Scale: Improved scalability and control
Hybrid clouds offer better scalability. So if you need to increase or decrease resources quickly, you can purchase more storage space on the public cloud without incurring additional management and technical overhead costs of servers that would only serve their purpose temporarily. This gives you more control over your storage space than most private cloud models. Some hybrid cloud providers even offer PaaS, so you can “build” an application and let Google, for example, host it. They take care of all the requirements to make sure your app runs full speed: no servers, no storage, no scale, no CDN… You can focus on building your app and not the servers behind it.
Costs: Reduced cost for servers and storage
Although a hybrid cloud is more expensive than a public cloud, it’s more cost-effective than opting for solely private cloud architecture. With a private cloud, costs relating to management and maintenance increase quickly as your business grows. Hybrid models empower businesses to take advantage of affordable public cloud storage, while still using a private cloud to store sensitive data.
Security: Secure data—at all levels
Organizations can choose to store more sensitive data in on-premises data centers in the private cloud to maximize security and protect against malicious cyber attacks. Plus they can use their public cloud storage to process, manage, and analyze less sensitive data. Cloud providers like Google, AWS and Azure are some of the most secure on the market, and security is built into the system from inception.
You also have a great degree of control over their data and increased security as the potential for data exposure is reduced. Enterprises can decide where to store their data and workloads (in the public or private cloud) based on factors like compliance, security requirements, and policy.
Security teams can also standardize redundant cloud storage to improve disaster recovery and data insurance.
Challenges with hybrid cloud architecture
1. Larger initial investment (Well, sorta… Read below)
If you’re using your own data center or servers in one of your offices, you’ll need to invest in on-premises hardware as well as managing and maintaining the private cloud computing component of your hybrid cloud architecture. Although public cloud operations will offset some of the hardware costs, the costs of managing and maintaining a hybrid cloud infrastructure can be costly for some businesses.
But if you’re using purely hosted IaaS and PaaS. then the initial cost is a lot lower.
2. Lack of visibility over overall cloud environment
Cloud computing environments are complex, and when your cloud infrastructure is divided between two or more clouds, things become even more complicated. Because of this, a hybrid cloud infrastructure can make it challenging to establish clear visibility of your overall cloud environment, along with the systems, processes, apps, and platforms you need to manage.
This can result in critical issues like compliance regulation falling under the radar. This lack of visibility is relatively simple to overcome though—just make sure to invest in a third-party platform that provides a complete overview of your cloud infrastructure.
3. Network issues would affect performance level
Network issues can affect the performance level of hybrid cloud infrastructures when your business relies on active applications that run in the public cloud. Often you might need to add more interconnection bandwidth, and latency is another consideration.
Analyze the volume of traffic shared in your hybrid cloud environment so you can construct a network that’s capable of maintaining the environment over low-latency network connections.
Purely hosted cloud architecture: A better option for businesses?
Although hybrid cloud UCaaS and CCaaS deployments offer different benefits for businesses, they’re not the only way to go. There are also purely cloud-hosted services that are a good choice for businesses of all shapes and sizes.
For example, you could use a hosted communications and collaboration platform, which allows you to do things like make phone calls, start video meetings, and send instant or SMS messages, all in one app, from anywhere.
👉 Dialpad tip:
That’s what InfoTrack did. See how they moved away from their clunky and expensive on-premises infrastructure, and moved to a cloud contact center platform to serve their customers better and provide excellent customer support remotely.
Cloud migration allows organizations to scale their infrastructure up or down depending on usage, business requirements, and company growth. What’s more, you can pay for the service on an as-needed basis, which can significantly reduce your costs.
Using business software and apps that are built on cloud architecture also means you can do things like instantly provision new users and spend way less time on installation and configuration.
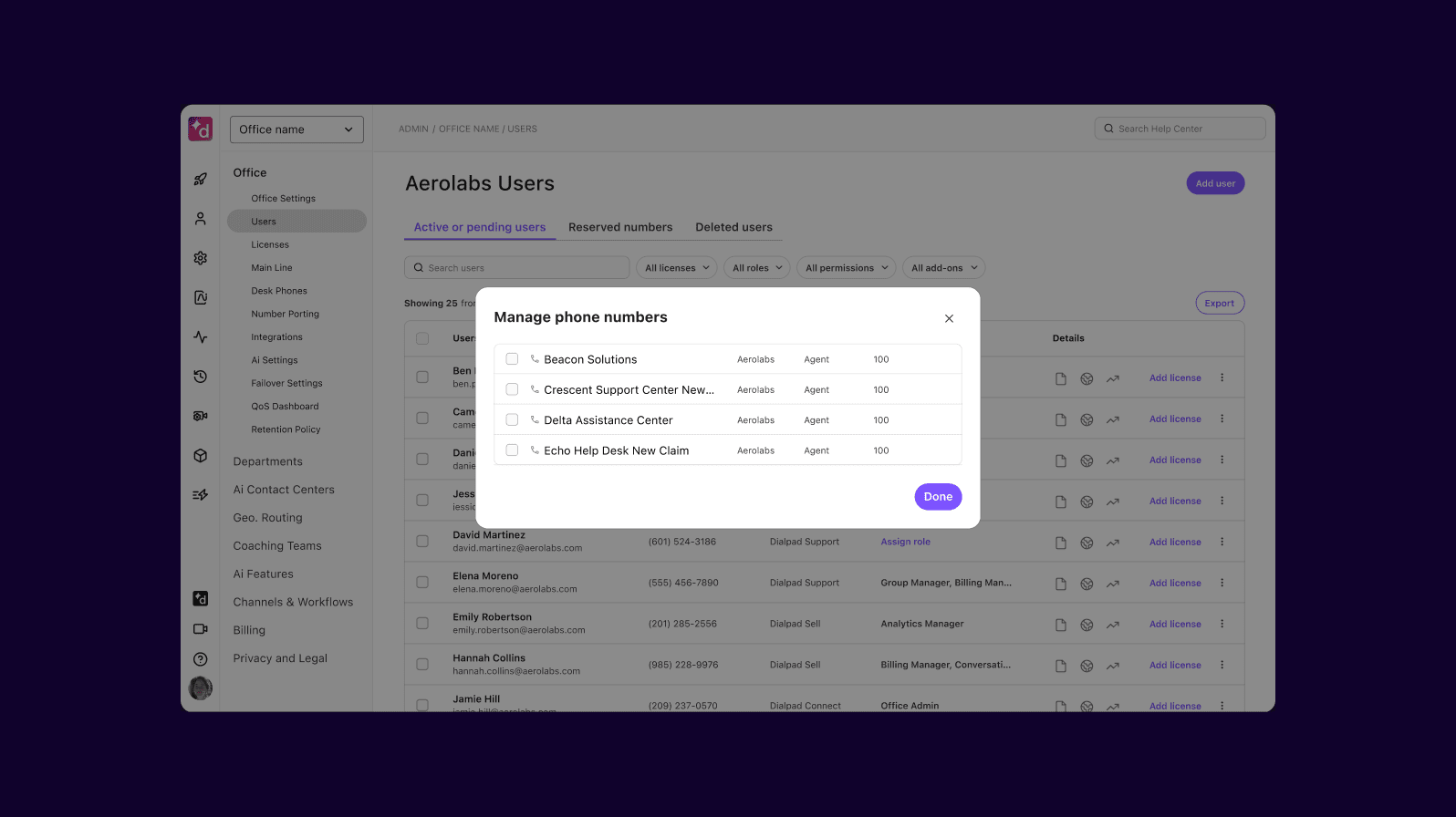
For example, Dialpad lets you add new users and new phone numbers right in your online account, in just a few clicks—a process that usually takes days, if not weeks:
3 signs you should consider a purely hosted cloud infrastructure
1. Security and privacy are extremely important to your customers
Cloud security involves a set of policies, role-based access, authentication, controls, procedures, and technologies that combine to protect cloud-based systems.
These security measures are put in place to protect cloud data, protect customer information, support regulatory compliance, and establish authentication rules for users and devices. Rules can be managed from a single console, which reduces administration overheads and empowers IT teams to focus on other aspects of the business.
🔒 Did you know?
Dialpad has a very comprehensive approach to cloud security, and uses the Google Cloud Platform to store and protect customer data. Permanent data, including contact lists, call records, recordings, and transcripts, are stored in Google Cloud Storage to ensure data storage is backed up, distributed, and protected even if disaster strikes.
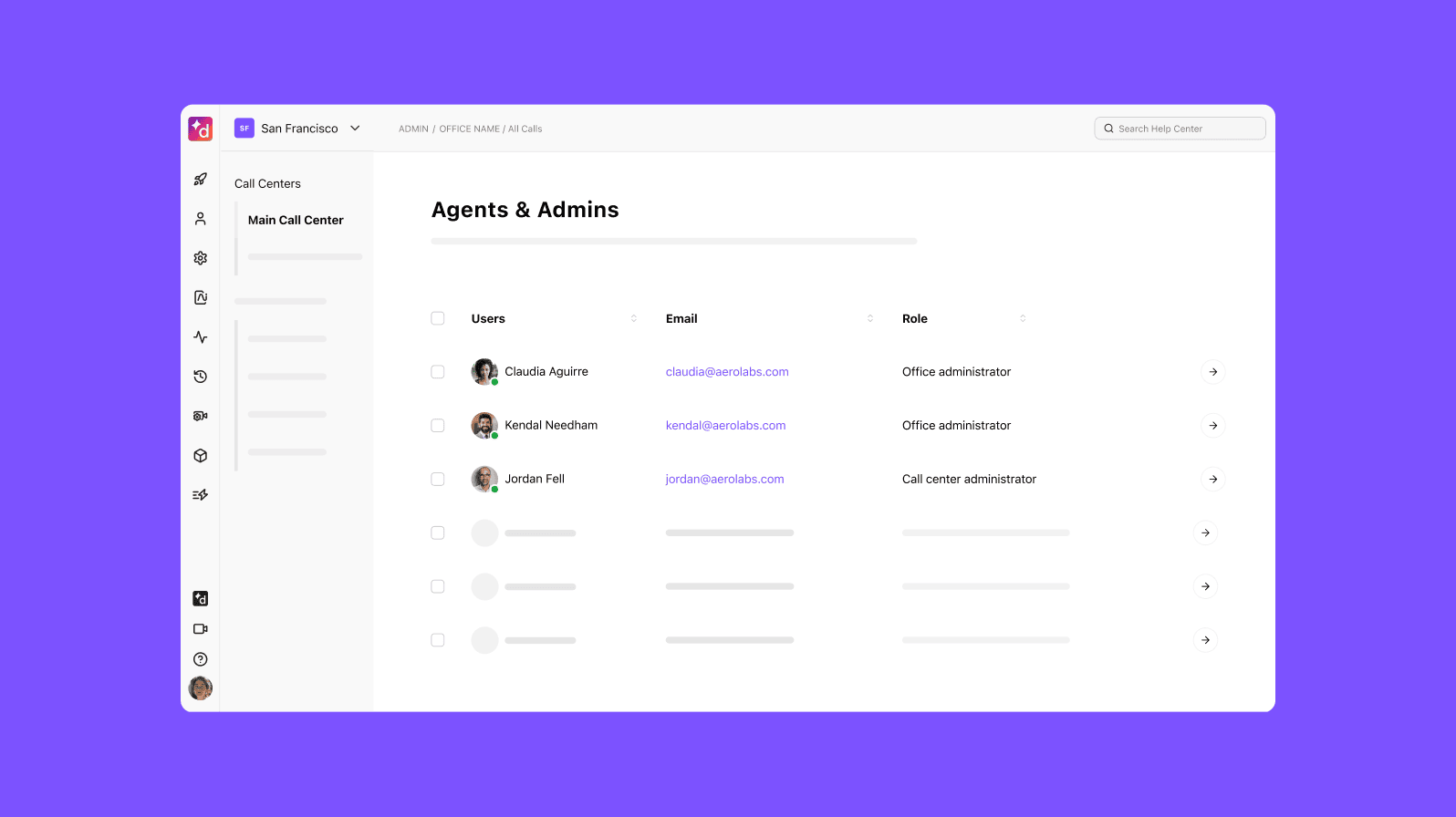
2. You need a solution that can scale quickly with you
One big benefit of purely hosted cloud solutions is that they empower businesses to increase or decrease IT resources like data storage, processing power, and networking quickly and effectively—without causing downtime.
Again, with Dialpad, when you need to add or remove users or expand your cloud storage capacity, you can do that with a single click in your account. Spinning up a new contact center team or adding agents to different departments? You can do that in just a few minutes.
3. You use a lot of software and hardware that need to be centralized
If your business relies on tons of software solutions and hardware equipment, you’ll benefit from centralizing it in a fully hosted cloud infrastructure. This way, everything you and your team need is easily accessible through a unified interface—no more toggling between apps or worrying about the lifecycle of your equipment or hardware.
This is also why it’s useful to have versatile cloud solutions that can do different things well. Instead of having one tool for video conferencing and another for instant messaging, and so on, you could use a solution that brings all those communication channels under a single app:

Not only does this help your team work more efficiently and productively, it’s a weight off your IT team’s shoulders as they won’t have to deal with managing all those different tools.
5 must-dos for optimal cloud management
1. Measure your system capacity vs usage
Cloud managers must measure and understand their system capacity and usage to outline which workloads and applications will run on which type of cloud. This includes what the work assignments do, how end-users interact with them, how their data is managed, how long they run for, the network they operate on, and more.
Determining system capacity and usage will help you to manage cloud storage and processes to optimize the full potential of your cloud infrastructure.
2. Focus on understanding the system security and policy management
Before transitioning to the cloud, try to get an understanding of the system security and policy management offered by your cloud service provider.
System security and its impact on cloud performance
Understand how your system’s security might affect the performance of your cloud system. For instance, data encryption processes can sometimes lower cloud performance. Consider investing in performance monitoring tools to keep this controlled.
Policy management and execution of cloud system governance
Hybrid cloud managers must remain informed about the written policies of cloud system governance to ensure they don’t encounter any problems with operations.
3. Build a “single pane of glass” to manage cloud services
Invest in tools that enable you to manage multiple cloud services from a single interface. This will allow administrators to transfer workloads and apps efficiently between clouds, saving time, energy, and resources.
4. Use SLAs as a guide to set expectations within hybrid cloud
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) refer to contracts between end-users and hybrid cloud managers and providers. They stipulate the level of service being provided and outline the penalty risk if they aren’t provided.
Although there are some expectations on the service provider to take responsibility for meeting their SLAs, it’s also the cloud manager’s role to ensure your own system delivers the promised services.
5. Work with your provider to maximize the potential of available tools and features
Work with your provider to familiarize yourself with the tools available. This includes API, DevOps, resource, security, network, native platform management, and more. All these tools can help you to manage your cloud infrastructure more effectively.
Take control of your company data with the ideal cloud architecture
Choosing the right cloud strategy for your organization is no easy task.
For most organizations, this transition is essential for moving to a remote or hybrid work environment. Communications is one of the most important areas in a business to consider, and even though not every single business is ready to make that move, those that are should look into platforms that can handle a range of business communications use cases in the cloud.
This will make connecting remote teams easier, and allow work-from-home agents to handle customer interactions effectively, no matter where in the world they are.
Ready to migrate your on-premises IT infrastructure to the cloud?
If you're thinking about a cloud communications solution, book a product tour of Dialpad to see if it’s a good fit for your business communication needs!
