Tags
Share
Businesses of all sizes, across all industries, are starting to increasingly incorporate AI into their everyday workflows and processes.
But for large global organizations with, say, 10,000+ employees, there are some extra considerations to keep in mind when vetting and allowing employees to use AI tools. So, what should business leaders and IT departments look out for when it comes to enterprise artificial intelligence? What are the differences between your average AI software and AI for enterprise?
Below, we‘ll delve into what enterprise AI is, how our team at Dialpad is building our own AI enterprise tools, and what to look for when shopping for an enterprise AI solution.
What is enterprise AI?
Enterprise AI refers to the use of artificial intelligence, or AI, technologies by large organizations or businesses, which are commonly known as enterprises. This is usually defined by company size—depending on how you define “enterprise,” it could be a company with anywhere from 5,000+ to 10,000+ employees.
Like regular AI tools, enterprise AI solutions can automate a variety of routine, repetitive tasks, and use machine learning (ML) algorithms to learn from data, adapt, and improve their performance over time without explicit manual programming.
Enterprise AI vs. non-enterprise AI:
Key differences There are a few key distinctions between enterprise AI and non-enterprise AI in the scale, scope, and purpose of their applications. Here's a breakdown of each of these differences:
Enterprise AI | Non-enterprise AI | |
Scope | Enterprise AI is designed to address the comprehensive needs of large organizations. It involves implementing the enterprise AI application across the entire organizational ecosystem, which impacts various departments, processes, and functions. | Non-enterprise AI, on the other hand, typically focuses on specific tasks, functions, or departments within a business—without necessarily aiming to transform the entire organizational structure. |
Scale | The scale of enterprise AI is typically global and spans multiple offices and thousands of employees worldwide, as it aims to optimize and transform the entire business operation. This typically involves handling vast datasets. For example, an enterprise AI transcription tool may be able to transcribe all of an enterprise’s calls in real time, whereas a similar non-enterprise tool would only be able to handle a few calls at once, and not necessarily in real time. | Non-enterprise AI applications usually operate on a smaller scale. For example, an AI tool that wasn’t designed for enterprise use may not be able to onboard a large number of users as quickly or as easily as enterprise AI software. |
Integrations | Enterprise AI technology should be able to integrate seamlessly with existing systems and processes within an organization. This is often complex and involves compatibility with legacy systems, adherence to data governance policies, and ensuring minimal disruption to ongoing operations. | Non-enterprise AI applications may be standalone solutions that do not necessarily integrate with an organization's existing technology infrastructure. They may not have SSO (single sign-on), for instance, or may require custom APIs or extensive modifications to existing systems before they can be used. |
Scale of data handling | Large organizations deal with massive datasets, and enterprise AI technology is designed to handle and analyze this amount of data. The scale of data processing in enterprise AI is often more extensive, involving data from various sources and departments. | Non-enterprise AI applications may operate on smaller datasets that are relevant to their specific use case, or if they don’t have enough data, may have to rely on third-party LLMs which result in additional costs and certain usage gaps, which limits those applications’ outputs. |
Customization and flexibility | Enterprise AI solutions provide a high degree of customization to meet the diverse needs of different organizations. For example, an enterprise AI writing tool may have the ability to “learn from” a company’s own content and style guides in order to generate highly customized content. | Non-enterprise AI applications usually have a more general approach. While some level of customization may be possible, it might not be as extensive as in enterprise AI. Taking the AI writing tool example, a non-enterprise AI tool may not be able to tailor the content that it generates based on a company’s specific data sets. |
The principal benefits of enterprise AI
For companies with a large number of employees and more strict security requirements, enterprise AI provides a few benefits:
Improved data analysis and easier access to actionable insights
Enterprise AI empowers organizations to make more informed decisions backed by comprehensive data analysis. One of the biggest hurdles for large-scale companies today is the unprecedented amount of data they now have access to. Enterprise AI can help business leaders and users in general save both time and effort when it comes to data analysis—the AI’s advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms can help extract valuable insights from those huge datasets in minutes or even seconds instead of days or weeks.
More accurate forecasting and predictive capabilities
Enterprise AI tools can also help organizations with forecasting performance more accurately, from sales to customer support. Instead of forecasting the traditional way with spreadsheets and manual calculations, AI can instantly ingest data and provide accurate forecasts for, say, a revenue org that needs to determine whether the company is in danger of missing its lead numbers this quarter.
Global scalability
Enterprise AI solutions are designed to scale readily with the constantly growing needs of large organizations. Whether it's handling increasing volumes of data or spinning up a new department or a thousand new licenses in the platform, enterprise AI offers a much higher level of scalability that’s suited to the dynamic environments of large-scale corporations.
Cost savings
While the initial investment in enterprise AI implementation can be pretty substantial, the long-term benefits are worth it—and often translate into significant cost savings. How? Well, the automation that AI makes possible can reduce labor costs and help companies allocate their resources more efficiently.
For example, Randstad, the world’s largest recruiting firm, manages over 600,000 candidates at any given time across its global recruitment centers—which means its team needs call center software for enterprises. Randstad’s recruiting team uses Dialpad’s enterprise AI solution to both save time and get more candidates through the door more quickly. “Dialpad’s AI-powered features have helped us save 10% of time and speed up the candidate screening process,” says Rinio Veeris, IT Specialist.
Challenges of AI that enterprises should be aware of
Despite all the benefits, there are some potential challenges and considerations that should be addressed proactively when implementing enterprise AI:
Cultural shift and employee resistance
Introducing enterprise AI often necessitates a cultural shift within organizations. Many employees may resist the change due to the fear of job displacement or skepticism about what AI tools can actually do. Business leaders should have a robust change management strategy and communication plan in place ahead of time to overcome this challenge.
Data privacy and security
AI systems, like any technology, are susceptible to security threats. Even though OpenAI has released ChatGPT Enterprise for enterprise use, its additional security features don’t answer all the concerns that have been brought up. For example, OpenAI still hasn’t clarified what kind of data was used to train its model, and there are still several lawsuits underway alleging that OpenAI used copyrighted material to train ChatGPT—a topic of concern for many enterprises.
An alternative to this would be to use enterprise AI that is built on private LLMs like DialpadGPT, which are highly specialized and built for enterprise use—not mainstream public use—which means they’re also generally more secure than consumer-grade LLMs, which leads us to the next point.
Data quality and governance
The success of any AI initiative hinges on the quality of data. (“Garbage in, garbage out.”) One of the biggest risks of using third-party LLMs—even if you’re using an enterprise version—is that even at that level, you’re not being told what is in the training datasets. It’s essentially a black box. For large organizations that are already dealing with vast datasets from multiple sources, this makes data quality and governance even more critical.
Establishing robust data governance practices not only ensures the accuracy and reliability of your enterprise AI tool’s data and outputs, it also protects your company and employees who will be using and sharing these outputs.
Regulatory and compliance issues
The use of AI raises legal and ethical dilemmas, especially in heavily regulated industries such as healthcare and finance. Enterprise AI tools should ensure transparency and accountability, and be trained ethically to minimize bias to mitigate potential legal risks and maintain public trust. For example, Proliance Surgeons, a surgical practice with over 80 care centers across the United States, uses an enterprise AI tool to transcribe conversations and voicemails.
Integration with existing systems
Implementing enterprise AI can be a complex process—you have to make sure you can smoothly integrate AI into your existing systems, ensure that data gets synced accurately, and so on. For large organizations with already sizeable tech stacks, this is one of the biggest hurdles the IT team has to face.
Effects on jobs and skill development
Building and using enterprise AI solutions require specialized skills. We’re already seeing large organizations starting to invest more in developing or hiring talent with expertise in machine learning, data science, and AI development (or training existing employees to bridge the skills gap).
Speaking of talent and the workforce, one risk that leaders should be aware of is to not give in to the temptation of over-relying on AI too soon. While AI can significantly speed up decision-making processes, we still need human oversight to make sure the AI’s outputs are valid and/or safe. For example, an architecture and engineering firm using AI to draw up blueprints can save a lot of time, but someone should still be reviewing those generated blueprints to make sure the measurements are correct—otherwise, there could be catastrophic consequences.
What to look for from an enterprise AI platform
With so many tools claiming to be enterprise AI platforms popping up almost every day, it’s critical to know how to tell true enterprise AI applications apart from the others. Here are a few considerations and features to look for when evaluating potential solutions:
A proof of concept (POC)
A good enterprise AI platform should make it easy for you to demonstrate the benefits of the solution to your C Suite. Any CIO worth their salt is likely going to ask for a POC before they sign any subscription or purchase agreement—if your potential AI tool doesn’t make it easy to set up a POC, that’s a red flag that they’re probably for smaller companies and not designed with enterprise use cases in mind.
(This is actually one of the five key steps our CIO, Prashanti, recommends when shopping for an AI solution.)
Robust machine learning capabilities
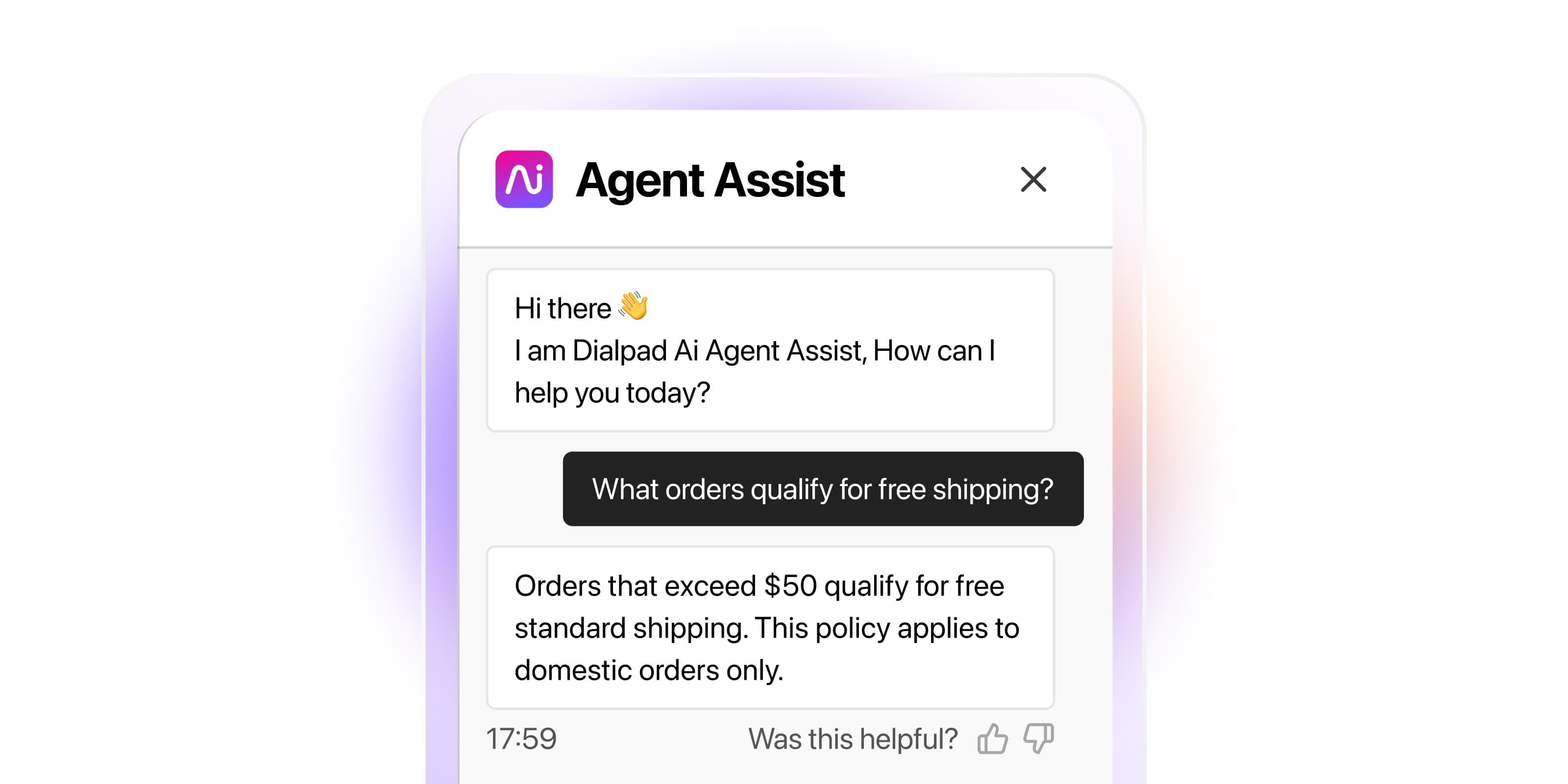
An effective enterprise AI platform must have robust machine learning capabilities at its core. Look for platforms whose models support continuous learning. The company may not advertise it, but make sure you ask the sales team whether the tool has its own LLM or is using an existing public LLM (like ChatGPT). A good enterprise AI solution will more often than not invest in developing its own LLM using its own training data—not a third party’s—for better accuracy and security.
Intuitive user experience
One thing that is often overlooked, especially when it comes to enterprise tech stacks, is the user experience: how easy is the tool to use? An intuitive user interface is essential for ensuring that employees across your various departments actually want to use (and end up adopting) the expensive enterprise AI platform you just bought 2,000 licenses for.
Security and reliability
Given the sensitivity of company data (and customer data) involved, robust data governance and enterprise-grade security features are non-negotiable in any enterprise AI solution. The platform should comply with your industry standards and regulations, provide access controls, and have audit trails to safeguard organizational data. For example, if you work in healthcare, your enterprise AI tool should be HIPAA-compliant.
Besides security, reliability is another critical consideration for enterprises, especially if they’re considering tools like enterprise VoIP or security platforms where you can’t afford to have downtime. This was one of the weaknesses of ChatGPT—companies using it were limited by usage caps, although if you can afford ChatGPT Enterprise licenses, OpenAI will remove these usage caps. Regardless, enterprise AI solutions should have some type of uptime guarantee. Dialpad’s AI customer intelligence platform, for instance, has a 100% uptime guarantee.
Ethical AI and bias mitigation
Even though this isn’t always at the top of the priority list, any AI enterprise solution should be able to clearly explain the ethical considerations behind how they built or designed their solution. Again, this is something that you have no control over or ability to dig into if you’re using an AI tool whose “AI” comes from a third-party LLM.
This means you won’t have any visibility into how the AI tool mitigates bias in its algorithms (if it does at all), promotes transparency, or adheres to ethical standards. Workday, for example, failed to mitigate its AI’s bias against Black and older job applicants. (Learn more about the steps our team takes to ensure we’re minimizing bias as much as we can as we’re building Dialpad Ai.
Ease of implementation and set up across large, dispersed workforces
It can be difficult to roll out a new tool in any new business, let alone a large global business with thousands or tens of thousands employees. Make sure your enterprise AI tool’s onboarding process clearly lays out a smooth transition with minimal disruptions to ongoing operations.
And on a related note, this user-friendliness extends to the scalability and flexibility side as well. Does the AI tool make it easy for you to add and remove users, set up new teams, and so on—across a globally dispersed user base?
With Dialpad, for example, we can add and remove users with just a few clicks from the online dashboard:
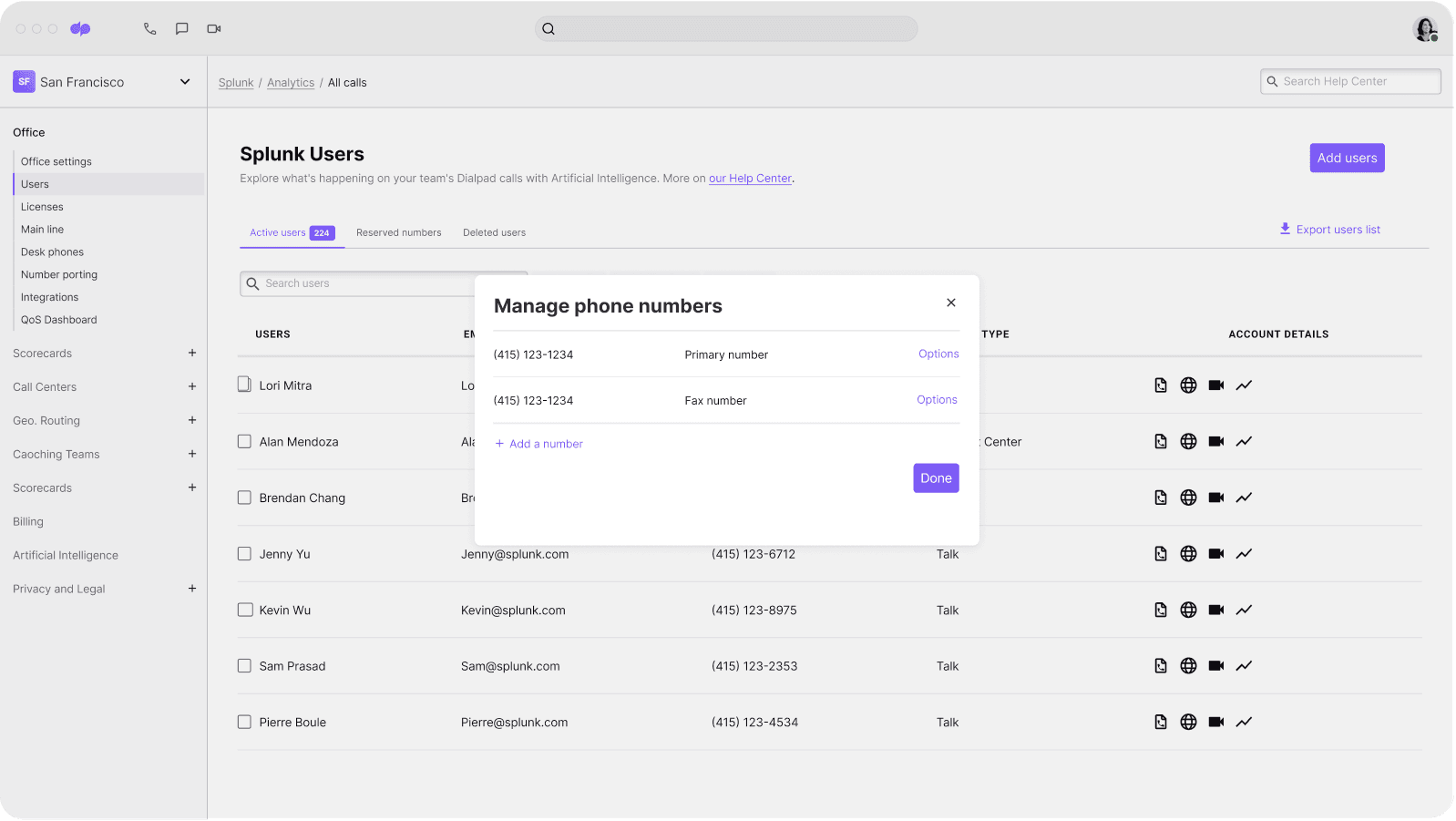
This means that if a company has to spin up a new contact center for the holidays to handle the huge increase in call and messaging volume, they can easily add those hundreds or thousands of seasonal employees quickly—and then remove them just as quickly once the busy season is over.
24/7 international support
Of course, it’s nearly impossible to roll out enterprise tools with absolutely zero hitches. That’s just the reality. No matter how polished your product and how experienced the onboarding team, sometimes things just happen. That’s why it’s critical to have 24/7 support—not just in the US, but worldwide. Dialpad, for example, offers 24/7 support for Enterprise plan customers over the phone and live chat.
Connect and empower your global teams with enterprise AI from Dialpad
Even though it’s still pretty early days, enterprise AI has the potential to be a transformative force for large organizations, offering unparalleled benefits in terms of efficiency, more data-driven decision-making, and a competitive edge.
To select the right solution for your specific organization, make sure to carefully vet the factors that set enterprise AI tools apart from regular AI tools—specifically, areas like security, scalability, whether the AI is proprietary or linked through a third party, and so on.
That being said, there is a huge variety of enterprise AI tools designed to help with everything from content creation to fostering enterprise collaboration to data analysis to customer experience and more. If your enterprise is curious about how AI can help improve your customer experience, Dialpad Ai can help your sales and support teams glean more conversational insights from your everyday conversations with customers, pinpoint coaching opportunities for sales reps and support agents, and much, much more.
Want to learn more about Dialpad for enterprises?
See how organizations like Randstad and Splunk are using Dialpad’s enterprise AI platform to scale their teams and uncover valuable insights in real time!









